| |
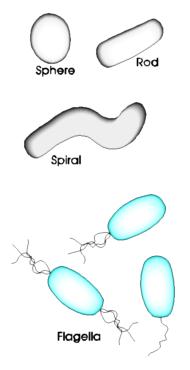
BACTERIAshapes are varied. Rod averages 1.5 to 3.0 microns long. Sphere diameters range from 0.5 to 1.0 microns. FLAGELLAare the wiggling filaments generally believed to be responsible for motility (movement) of most free-swimming bacterial cells. |
 |
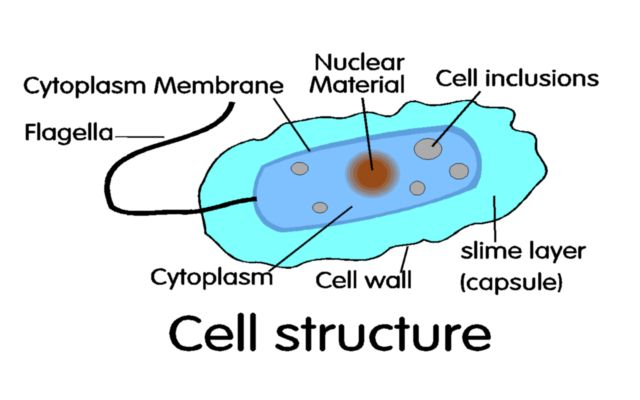 BACTERIAL CELL STRUCTUREis best studied in rod form bacteria. Capsule or slime layer is formed by decomposition of the cell wall. | |
FUNGItend to be filamentous. These non-photosynthetic plants use organic matter for their carbon and energy. |
 |
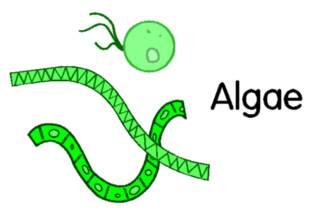
ALGAEare often green (with many other colors found) and have many shapes. Unlike fungi and bacteria, they use light for their energy. |
 |
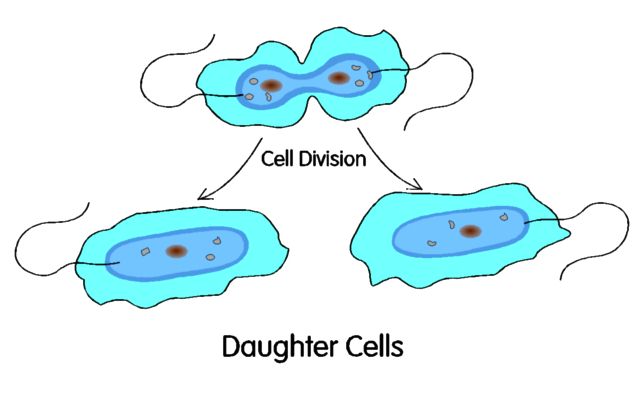
Cell Division | |
Bacteria feed by absorption through their cell membranesIn the first stage, they secrete enzymes (extra-cellular)
which break down the large particulates and solids. Bacteria constantly
produce enzymes. This process will produce CO2 and H2O and seed bacteria since cell division occurs when sufficient food is processed. Time and oxygen are very important when bacterial inoculants are employed. | |